論文雑誌「Analyst」のカバーピクチャーを制作しました[東京工業大学]
弊社で制作しました東京工業大学 上田 宏先生ご依頼のカバーアートが、
イギリスの王立化学会発行の学術雑誌 Analyst 2022年11月号に選ばれました。
Client
東京工業大学
科学技術創成研究院 化学生命科学研究所
上田 宏先生
科学技術創成研究院 化学生命科学研究所
上田 宏先生
Journal
Analyst
21 November 2022 Link
21 November 2022 Link
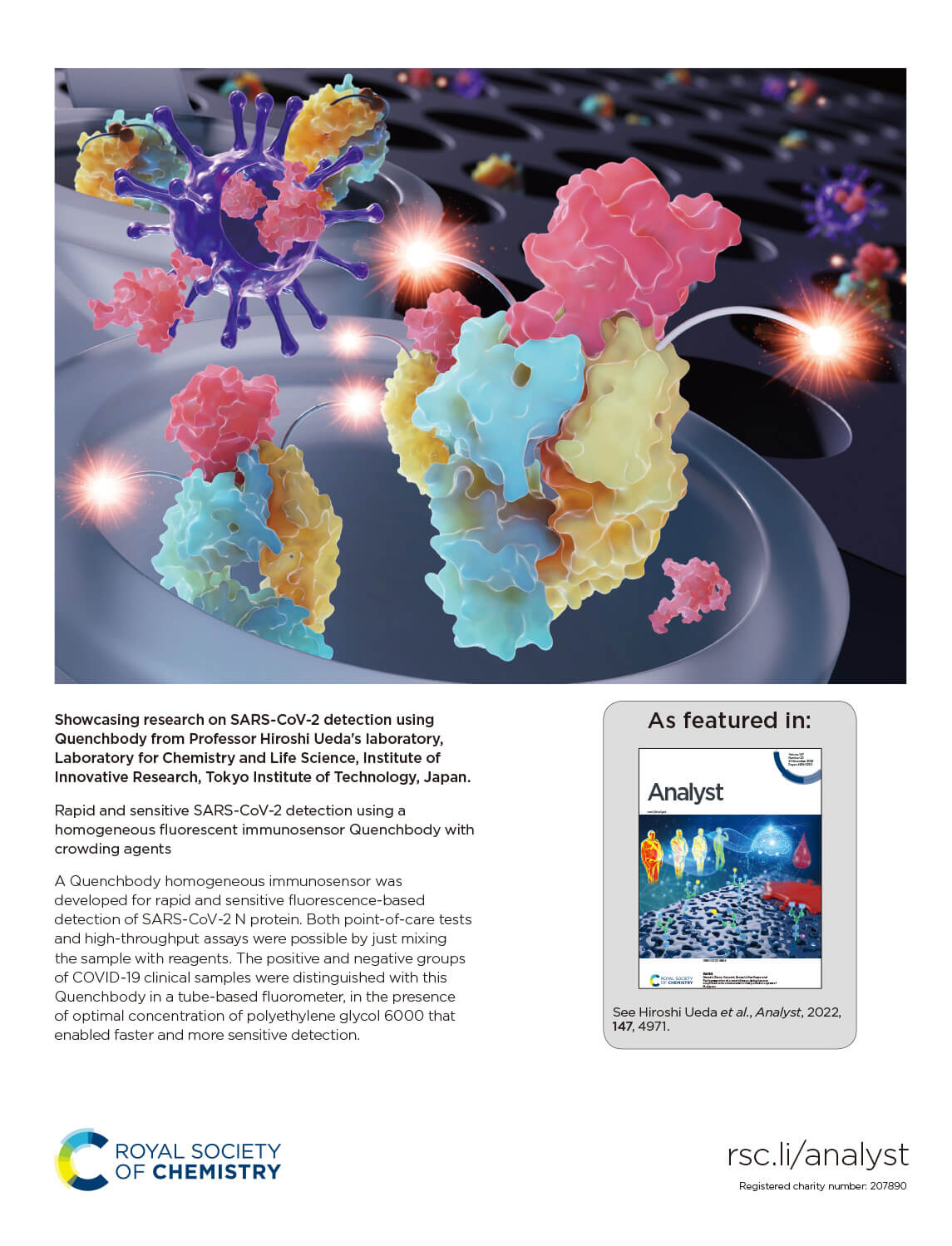
Rapid and sensitive SARS-CoV-2 detection using a homogeneous fluorescent immunosensor Quenchbody with crowding agents
Bo Zhu, Nobuyuki Nosaka, Shuji Kanamaru, Jinhua Dong, Yancen Dai, Akihito Inoue, Yinghui Yang, Kaori Kobayashi, Tetsuya Kitaguchi, Hiroshi Iwasaki, Ryuji Koike, Kenji Wakabayashi and Hiroshi Ueda
Antigen tests for SARS-CoV-2 are widely used by the public during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, which demonstrates the societal impact of homogeneous immunosensor-related technologies. In this study, we used the PM Q-probe and Quenchbody technologies to develop a SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N protein) homogeneous immunosensor based on a human anti-N protein antibody. For the first time, we uncovered the crowding agent's role in improving the performance of the double-labeled Quenchbody, and the possible mechanisms behind this improvement are discussed. The 5% polyethylene glycol 6000 significantly improved both the response speed and sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Quenchbodies. The calculated limit of detection for recombinant N protein was 191 pM (9 ng mL−1) within 15 min of incubation, which was 9- to 10-fold lower than the assay without adding crowding agent. We also validated the developed immunosensor in a point-of-care test by measuring specimens from COVID-19-positive patients using a compact tube fluorometer. In brief, this work shows the feasibility of Quenchbody homogeneous immunosensors as rapid and cost-efficient tools for the diagnosis and high-throughput analysis of swab samples in large-scale monitoring and epidemiological studies of COVID-19 or other emerging infectious diseases.
Link
Bo Zhu, Nobuyuki Nosaka, Shuji Kanamaru, Jinhua Dong, Yancen Dai, Akihito Inoue, Yinghui Yang, Kaori Kobayashi, Tetsuya Kitaguchi, Hiroshi Iwasaki, Ryuji Koike, Kenji Wakabayashi and Hiroshi Ueda
Antigen tests for SARS-CoV-2 are widely used by the public during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, which demonstrates the societal impact of homogeneous immunosensor-related technologies. In this study, we used the PM Q-probe and Quenchbody technologies to develop a SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N protein) homogeneous immunosensor based on a human anti-N protein antibody. For the first time, we uncovered the crowding agent's role in improving the performance of the double-labeled Quenchbody, and the possible mechanisms behind this improvement are discussed. The 5% polyethylene glycol 6000 significantly improved both the response speed and sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Quenchbodies. The calculated limit of detection for recombinant N protein was 191 pM (9 ng mL−1) within 15 min of incubation, which was 9- to 10-fold lower than the assay without adding crowding agent. We also validated the developed immunosensor in a point-of-care test by measuring specimens from COVID-19-positive patients using a compact tube fluorometer. In brief, this work shows the feasibility of Quenchbody homogeneous immunosensors as rapid and cost-efficient tools for the diagnosis and high-throughput analysis of swab samples in large-scale monitoring and epidemiological studies of COVID-19 or other emerging infectious diseases.
Link
